Enterprise Architecture
- Part 1:What is Enterprise Architecture
- Part 2: Purpose and benefit of Enterprise Architecture
- Part 3: Layers of Enterprise Architecture
- Part 4: Enterprise Architecture Frameworks and Methodologies
- Part 5: Use cases of Enterprise Architecture
- Part 6: How to Create Enterprise Architecture in EdrawMax
- Part 7: Tips for Enterprise Architecture
- Part 8: Example
Part 1: What is Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise architecture (EA) applies the architectural techniques and principles on strategic design and planning in a corporate/business context. This is a strategically laid out practice to conduct enterprise analysis, design, planning, and implementation.
Enterprise Architecture aims to successfully medium to large scale organizations by reducing redundancy, conflicts, complexity, and business risks. It also introduces standards across departments and teams to make the efforts unified and geared towards common goals.
Enterprise architects perform the analysis of enterprise structure and processes to support drawing information and conclusions from the data collected through enterprise architecture. This sharing of resources later on results in efficiency, agility, and no conflict among the stakeholders.
Part 2: Purpose and benefit of Enterprise Architecture
Enterprise benefit supports the overall strategic process in the organization to promote efficiency, sharing of resources without conflict, and decreased risks. Here is a list of some more benefits of enterprise architecture in detail.
- The most relevant technology, especially in the information technology field, currently is agile development. Enterprise architecture supports the implementation of enterprise-wide agile methodologies. It accelerates product development and deployments in organizations in general and in IT organizations in particular.
- Enterprise architecture provides a strong base for no-conflict information and data sharing in enterprises. This data-driven process gives the decision-makers an insight to make successful investments and strategies.
- Birthday surprises are pleasant; however, surprises in the organization may result in mayhem and a lack of decision-making. When organizations use a formal and robust structure for running their business, eventually, they can make a support system based on data. This system can predict problems and can also help to deal with surprise situations.
- A formal cost and benefit analysis can be conducted.
- Standardized processes help organizations to see the problems before they become a disaster. Also, a continuous improvement plan goes in parallel with the execution of organizational goals. It ensures that the change for the better is always in progress.
Part 3: Layers of Enterprise Architecture
Though enterprise architecture is a structure that can be widely customized, and every organization can tailor it accordingly to individual needs. However, there is a consensus that there are generally four layers of any enterprise architecture.
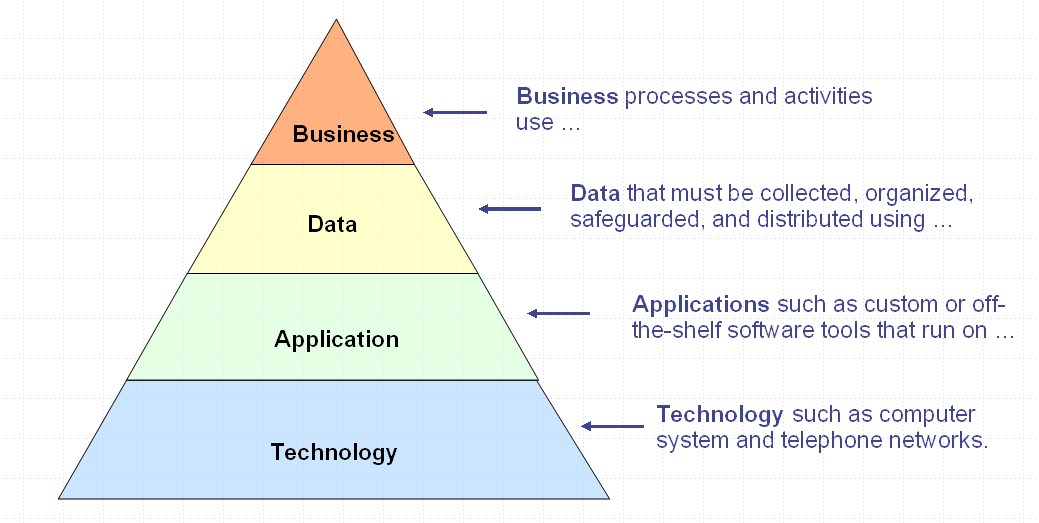
Business Architecture Layer
The business architecture layer describes the organizational structure. It states what functions are performed in the company and who performs what duty? It also makes a foundation for the business that becomes a reference point to go back to every challenging situation. It addresses the questions like;
Organization's vision, goals, and strategy to accomplish these goals?
What functions and processes are performed, and who is responsible for each?
Application Architecture Layer
This layer is functional. It describes the core business processes and individual applications. Now application architecture defines the relationship between these two primary components of an organization. The application architecture layer involves ensuring the applications and the integrations align with the organization's growth strategy.
Technology Layer
This is a layer that handles the implementation of the goals and objectives through software and hardware. It implements business, data, and application services.
Part 4: Enterprise Architecture Frameworks and Methodologies
An architecture framework outlines the principles and practices for creating and using the architecture for an organization or system. There are four powerful frameworks.
1. The Open Group Architectural Framework
The Open Group Architectural Framework is one of today's most common framework structures used in the field. Ir is a robust framework with a common vocabulary to use, recommended standards and compliance methods, suggested software and tools, and the best practices.
2. The Zachman Framework
The foundation of the Zachman Framework focuses on six descriptive foci and six-player perspectives.
The foci are data, function, network, people, time, and motivation. The perspectives are planner, owner, designer, builder, subcontractor, and enterprise.
It provides a structure with these twelve components to define how best your company can operate.
3. Federal Enterprise Architectural Framework
The federal enterprise architectural framework (FEAF) has five reference models: business, service, components, technical, and data. These five models combine to determine the best way to install enterprise architecture.
4. Gartner
Gartner implements a single unified entity that combines business owners, information specialists, and technology implementers. Gartner has its basis in continuous improvement through re-correction to tackle any oncoming problems.
Part 5: Use cases of Enterprise Architecture
Data security/risk management.
Data is one of the most precious assets a company has in current times. Therefore, enterprise architecture's vital function is data security which is dealt with in the data architecture layer of the EA. Enterprise architecture makes sure that data security is proactive and not reactive. Enterprise architecture maintains security planning.
Data governance.
Data governance makes it possible to take advantage of data opportunities that may result in minimizing data risks, smooth and conflict-free execution of objectives along with increased revenue.
Post-merger harmonization
Mergers are generally tricky situations. It can result in jeopardized functions, an unsatisfied workforce, and confused operations. An enterprise architecture ensures that the involved parties have access to all data and strategic planning tools and inputs to give a clear picture of situations.
A well-maintained enterprise architecture supports and promotes a long successful merger of departments and companies.
Part 6: How to Create Enterprise Architecture in EdrawMax
1. Launch EdrawMax software.
2. Go to New>Business>Enterprise Architecture.
3. You can draw enterprise architecture from scratch here. Use the symbols from the symbols library.
4. Alternatively, you can use the pre-made templates to build your EA from a model. For using templates, go to Templates>Business>Enterprise Architecture and choose a template for yourself.
EdrawMax
All-in-One Diagram Software
- Superior file compatibility: Import and export drawings to various file formats, such as Visio
- Cross-platform supported (Windows, Mac, Linux, Web)
Part 7: Tips for Enterprise Architecture
- Always have a complete analysis of the situation before designing an enterprise architecture. This includes evaluation of current risks and challenges along with the future goals, outcomes, and deliverables.
- Always build a custom enterprise architecture based on the company's requirements.
- Make a framework for measuring success to give a numerical picture of the theory.
Part 8: Example
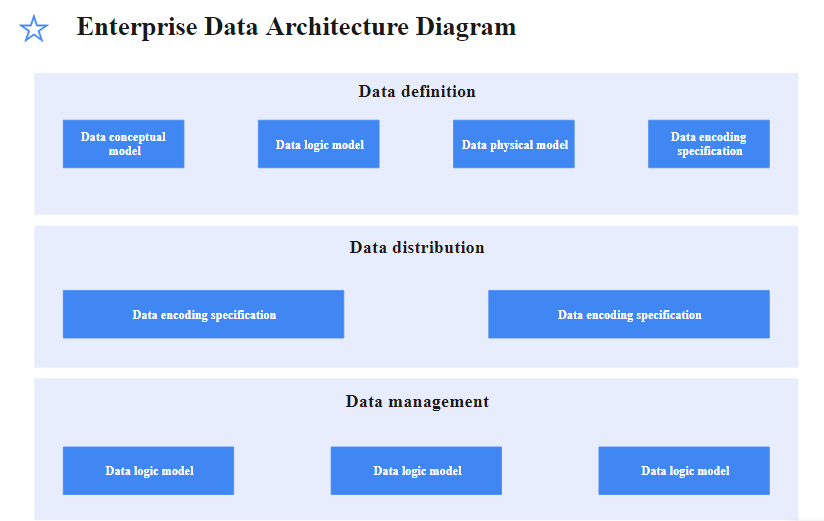
This enterprise data architecture diagram depicts the data layer of an EA. It has three layers called data definition, distribution, and management. These layers are further divided into other models. The content is concise but may contain further details as attachments.

